Case Formulation and Disorder-Specific Models
“[Formulation is] The lynch pin that holds theory and practice together” (Butler, 1998).Cognitive behavioral therapists use individually tailored formulations as a framework with which to understand their patients’ difficulties and to plan effective treatment. A case formulation helps therapists and patients to understand the origin, current status, and maintenance of a problem. Formulations are developed collaboratively between therapists and patients during the assessment phase of therapy and are revised as new information is gathered during the course of treatment. Jacqueline Persons wrote an influential account of individualized case formulation (1989). Her current case formulation approach (2008) describes how a complete CBT case formulation ties together all of the following parts:
all of a patient’s symptoms, disorders, and problems;
hypotheses about the mechanisms causing the disorders and the problems;
proposes the recent precipitants of the current problems and disorders;
describes the origins of the mechanisms.
Showing 1 to 50 of 108 results
Vicious Cycle - Responses And Consequences
Vicious Cycle - Responses And Consequences
Vicious Cycle - Costs And Benefits
Vicious Cycle - Costs And Benefits
CBT Model – Maintaining Processes – Past And Present
CBT Model – Maintaining Processes – Past And Present
CBT Model – Maintaining Processes
CBT Model – Maintaining Processes
What Keeps Death Anxiety Going?
What Keeps Death Anxiety Going?
What Keeps Fears And Phobias Going?
What Keeps Fears And Phobias Going?
What Keeps Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD) Going?
What Keeps Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD) Going?
Recognizing Specific Phobia
Recognizing Specific Phobia
Recognizing Social Anxiety Disorder
Recognizing Social Anxiety Disorder
Recognizing Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Recognizing Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Recognizing Panic Disorder
Recognizing Panic Disorder
Recognizing Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Recognizing Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Recognizing Insomnia Disorders
Recognizing Insomnia Disorders
Recognizing Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Recognizing Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Recognizing Bulimia Nervosa
Recognizing Bulimia Nervosa
Recognizing Anorexia Nervosa
Recognizing Anorexia Nervosa
Recognizing Depersonalization-Derealization Disorder (DPD)
Recognizing Depersonalization-Derealization Disorder (DPD)
Recognizing Prolonged Grief Disorder
Recognizing Prolonged Grief Disorder
Recognizing Hypochondriasis
Recognizing Hypochondriasis
Recognizing Hoarding Disorder
Recognizing Hoarding Disorder
Recognizing Complex Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
Recognizing Complex Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
Recognizing Body Dysmorphic Disorder
Recognizing Body Dysmorphic Disorder
Recognizing Binge Eating Disorder
Recognizing Binge Eating Disorder
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Health Anxiety (Salkovskis, Warwick, Deale, 2003)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Health Anxiety (Salkovskis, Warwick, Deale, 2003)
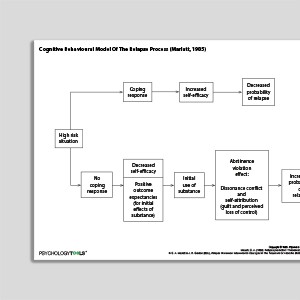
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of The Relapse Process (Marlatt & Gordon, 1985)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of The Relapse Process (Marlatt & Gordon, 1985)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Clinical Perfectionism (Shafran, Cooper, Fairburn, 2002)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Clinical Perfectionism (Shafran, Cooper, Fairburn, 2002)
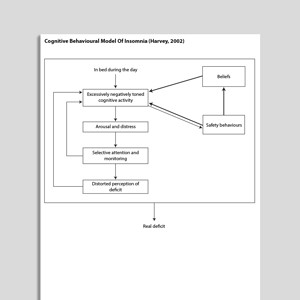
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Insomnia (Harvey, 2002)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Insomnia (Harvey, 2002)
What Keeps Perfectionism Going?
What Keeps Perfectionism Going?
What Keeps Bulimia Going?
What Keeps Bulimia Going?
What Keeps Depersonalization And Derealization Going?
What Keeps Depersonalization And Derealization Going?
What Keeps Anorexia Going?
What Keeps Anorexia Going?
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD: Ehlers & Clark, 2000)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD: Ehlers & Clark, 2000)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Social Phobia (Clark, Wells, 1995)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Social Phobia (Clark, Wells, 1995)
What Keeps Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) Going?
What Keeps Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) Going?
What Keeps Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Going?
What Keeps Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Going?
What Keeps Social Anxiety Going?
What Keeps Social Anxiety Going?
What Keeps Low Self-Esteem Going?
What Keeps Low Self-Esteem Going?
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Depersonalization (Hunter, Phillips, Chalder, Sierra, David, 2003)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Depersonalization (Hunter, Phillips, Chalder, Sierra, David, 2003)
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Formulation
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Formulation
Therapy Blueprint For Social Anxiety
Therapy Blueprint For Social Anxiety
Links to external resources
Psychology Tools makes every effort to check external links and review their content. However, we are not responsible for the quality or content of external links and cannot guarantee that these links will work all of the time.
Assessment
-
Collaborative Case Conceptualization Rating Scale (CCC-RS)
| Kuyken, Padesky, Dudley | 2009
- Kuyken, W., Beshai, S., Dudley, R., Abel, A., Görg, N., Gower, P., … & Padesky, C. A. (2016). Assessing competence in collaborative case conceptualization: Development and preliminary psychometric properties of the Collaborative Case Conceptualization Rating Scale (CCC-RS).Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy,44(2), 179-192.
- Rating scale & coding manual
- Score sheet & feedback form
Case Conceptualization / Case Formulation
- Formulation in Compassion Focused Therapy | Paul Gilbert | 2007
- Maxi formulation | Helen Moya
-
EMDR Case Formulation Tool
| Ines Santos | 2019
- Journal Article
- V1 – PDF
- V2 - PDF
- V2 - Word
- The “Blobby” formulation | Helen Kennerley | 2015
- Good practice guidelines on the use of psychological formulation | British Psychological Society: Division Of Clinical Psychology
- A quick guide to ACT case conceptualization | Russ Harris | 2009
- Outline of ACT assessment / case formulation process | Jason Luoma
- ACT simple case formulation | Julian McNally
- Team formulation: key considerations in mental health services | Association of Clinical Psychologists UK | 2022
- DBT Case Formulation Format | Comtois
- The case formulation approach to cognitive behavior therapy | Jacqueline Persons | 2014
- A case formulation approach to cognitive-behavior therapy | Jacqueline Persons | 2015
Information Handouts
- Cycle vs. Heart Illustration for EFT | Paul Sigafus | 2013
Information (Professional)
- Working with Schemas, Core Beliefs, and Assumptions | Frank Wills | 2008
Presentations
- EMDR: Using Case Formulation In Treatment Planning And Target Selection | Ines Santos | 2023
- Cafe formulation in cognitive-behavioral therapy | Caleb Lack
- The role of a case conceptualization model and core tasks of intervention | Donald Miechenbaum | 2014
Video
- CBT case formulation | Jacqueline Persons
- The Newcastle Model – A family guide for inpatient units | CNTW NHS Trust | BPS DCP FPOP | 2020
- Formulations used in the UK for the management of behaviours that challenge | Ian James | 2022
- Formulations In Dementia Care | CNTW NHS Trust | BPS DCP FPOP | 2020
Worksheets
- Case Formulation Template
Recommended Reading
Cognitive Behavioral Models Of Disorders
- Vlaeyen, J. W. S., & Linton, S. J. (2000). Fear-avoidance and its consequences in chronic musculoskeletal pain: a state of the art. Pain, 85(3), 317–332.
- Espie, C. A. (2002). Insomnia: conceptual issues in the development, persistence, and treatment of sleep disorder in adults. Annual Review of Psychology, 53, 215–243.
- Fairburn, C. G., Cooper, Z., & Shafran, R. (2003). Cognitive behaviour therapy for eating disorders: A “transdiagnostic” theory and treatment.Behaviour Research and Therapy,41(5), 509-528.
- Fennell, M. J. (1997). Low self-esteem: A cognitive perspective. Behavioral and Cognitive Psychotherapy, 25(1), 1-26.
- Fernie, B. A., Bharucha, Z., Nikčević, A. V., Marino, C., & Spada, M. M. (2017). A Metacognitive model of procrastination. Journal of Affective Disorders, 210, 196-203.
- Garety, P. A., Kuipers, E., Fowler, D., Freeman, D., & Bebbington, P. E. (2001). A cognitive model of the positive symptoms of psychosis. Psychological Medicine, 31(2), 189-195.
- Harvey, A. G. (2002). A cognitive model of insomnia. Behavior Research and Therapy, 40, 869–894.
- Heimberg, R. G., & Becker, R. E. (1981). Cognitive and behavioral models of assertive behavior: Review, analysis and integration. Clinical Psychology Review, 1(3), 353-373.
- Mansueto, C. S., Golomb, R. G., Thomas, A. M., & Stemberger, R. M. T. (1999). A comprehensive model for behavioral treatment of trichotillomania. Cognitive and Behavioral Practice, 6(1), 23-43.
- Marlatt, G. A. (1985). Relapse prevention: Theoretical rationale and overview of the model. In G. A. Marlatt & J. R. Gordon (Eds.), Relapse prevention (1st ed., pp. 280–250). New York: Guilford Press.
- Morrison, A. P. (2001). The interpretation of intrusions in psychosis: an integrative cognitive approach to hallucinations and delusions. Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy, 29(3), 257-276.
Social Anxiety Disorder
- Moscovitch, D. A. (2009). What is the core fear in social phobia? A new model to facilitate individualized case conceptualization and treatment. Cognitive and Behavioural Practice, 16. 123-134
Cognitive Behavioral Models Of Disorders
- Salkovskis, P. M., Forrester, E., & Richards, C. (1998). Cognitive–behavioral approach to understanding obsessional thinking.The British Journal of Psychiatry,173(S35), 53-63.
- Salkovskis, P. M., Warwick, H. M. C., Deale, A. C. (2003). Cognitive-Behavioral Treatment for Severe and Persistent Health Anxiety (Hypochondriasis).Brief Treatment and Crisis Intervention, 3, 353-367
- Ehlers, A., & Clark, D. M. (2000). A cognitive model of posttraumatic stress disorder. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 38(4), 319-345.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
- Wells, A. (1995). Meta-cognition and worry: A cognitive model of generalized anxiety disorder.Behavioural and cognitive psychotherapy,23(3), 301-320
Cognitive Behavioral Models Of Disorders
- Whalley, M. G., & Cane, D. A. (2017). A cognitive-behavioral model of persistent postural-perceptual dizziness. Cognitive and Behavioral Practice, 24(1), 72-89.
Team formulation
- Berry, K., Haddock, G., Kellett, S., Roberts, C., Drake, R., & Barrowclough, C. (2016). Feasibility of a ward‐based psychological intervention to improve staff and patient relationships in psychiatric rehabilitation settings. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 55(3), 236-252.
- What is the case formulation approach to cognitive-behavior therapy? | Jacqueline Persons | 2008
Case formulation / Case conceptualization
- Geisser, S., & Rizvi, S. L. (2014). The Case of” Sonia” Through the Lens of Dialectical Behavior Therapy.Pragmatic Case Studies in Psychotherapy,10(1), 30-39.
- Haynes, S. N., Leisen, M. B., Blaine, D. D. (1997). Design of individualized behavioral treatment programs using functional analytic clinical case models. Psychological Assessment, 9(4), 334-348
- Kuyken, W., Padesky, C. A., Dudley, R. (2008). The science and practice of case conceptualization. Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy, 36, 757-768
- Persons, J. B., & Lisa, S. T. (2015). Developing and Using a Case Formulation to Guide Cognitive-Behavior Therapy. Journal of Psychology & Psychotherapy, 5(2), 1
- Special issue: Team formulation. (2015). Clinical Psychology Forum, 275.
- Spencer, H. M., Dudley, R., Johnston, L., Freeston, M. H., Turkington, D., & Tully, S. (2022). Case formulation—A vehicle for change? Exploring the impact of cognitive behavioural therapy formulation in first episode psychosis: A reflexive thematic analysis. Psychology and Psychotherapy: Theory, Research and Practice.
Cognitive Behavioral Models Of Disorders
- Boelen, P. A., van den Hout, M. A., & van den Bout, J. (2006). A Cognitive-Behavioral Conceptualization of Complicated Grief. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 13(2), 109–128.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
- Borkovec, T. D., Alcaine, O., & Behar, E. (2004). Avoidance theory of worry and generalized anxiety disorder.Generalized anxiety disorder: Advances in research and practice,2004.
Cognitive Behavioral Models Of Disorders
- Chapman, A. L., Gratz, K. L., & Brown, M. Z. (2006).Solving the puzzle of deliberate self-harm: The experiential avoidance model.Behaviour Research and Therapy, 44(3), 371–394.
- Clark, D. M. (1986). A cognitive approach to panic. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 24(4), 461-470.
- Clark, D. M., & Wells, A. (1995). A cognitive model of social phobia.Social phobia: Diagnosis, assessment, and treatment,41(68), 00022-3.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
- Dugas, M. J., Gagnon, F., Ladouceur, R., & Freeston, M. H. (1998). Generalized anxiety disorder: A preliminary test of a conceptual model.Behaviour research and therapy,36(2), 215-226.
What Is Case Conceptualization / Case Formulation?
Types of Case Formulation
Case formulations can vary according to their purpose, and according to the information they attempt to convey. A number of types of formulation have been described:A cross-sectional formulation presents information relevant to a short time period, as though an event were sliced open at a particular moment in time to reveal the triggering event, thoughts (interpretations/appraisals), emotions, body feelings, and behaviors or reactions. One of the most popular formats for a cross-sectional formulation is Padesky and Mooney’s ‘hot cross bun’ (1990).
A longitudinal formulation presents information relevant to the origin and maintenance of a problem. Weerasekera’s “Multiperspective model” popularized the use of the “5 Ps” approach (presenting, predisposing, precipitating, perpetuating, and protective) to case formulation (Weerasekera, 1993). Judith Beck’s cognitive conceptualization (1995) links longitudinal factors (including relevant childhood data, core beliefs, conditional assumptions, coping strategies) to cross-sectional breakdowns (situation, automatic thought and appraisal, emotion, behavior).
Micro-formulations have been described as a helpful way of understanding the origin and effects of troubling imagery (Hackmann, Bennett-Levy, & Holmes, 2011). In this approach problematic images are explored along with their origin, associated appraisals, current impact, maintenance factors, and cognitive consequences.
Disorder-specific models describe the critical presenting, predisposing, precipitating, and perpetuating factors relevant to a condition. Disorder-specific cognitive behavioral conceptualizations have been published for most conditions including low self-esteem, panic, obsessive-compulsive disorder, psychosis, post-traumatic stress disorder.
References
Beck, J. S. (1995). Cognitive behavior therapy: Basics and beyond. New York: Guilford Press.
Butler, G. (1998). Clinical formulation. In A. S. Bellack and M. Hersen (eds) Comprehensive clinical psychology. New York: Pergamon Press
Hackmann, A., Bennett-Levy, J., & Holmes, E. A. (2011). Oxford guide to imagery in cognitive therapy. New York: Oxford University Press.
Padesky, C. A., & Mooney, K. A. (1990). Presenting the cognitive model to clients. International Cognitive Therapy Newsletter, 6, 13–14.
Persons, J. B. (1989). Cognitive therapy in practice: A case formulation approach. New York: WW Norton.
Persons, J. (2008). The case formulation approach to cognitive-behavior therapy (guides to individualized evidence-based treatment).
Weerasekera, P. (1993). Formulation: A multiperspective model. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 38(5), 351–358.