Anxiety
Fear and its associated reactions (freeze, flight, fight) can be useful responses to a dangerous or threatening situation. However, clients suffering from anxiety disorders experience these reactions too strongly, too often, or in inappropriate situations - and they can be distressing and exhausting. Psychology Tools can help you with CBT for anxiety - our anxiety worksheets are designed to help clients with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), health anxiety (hypochondriasis), panic disorder, phobias, and social anxiety.
What Keeps Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Going?
What Keeps Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Going?
What Keeps Social Anxiety Going?
What Keeps Social Anxiety Going?
What Keeps Low Self-Esteem Going?
What Keeps Low Self-Esteem Going?
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Depersonalization (Hunter, Phillips, Chalder, Sierra, David, 2003)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Depersonalization (Hunter, Phillips, Chalder, Sierra, David, 2003)
Understanding Health Anxiety
Understanding Health Anxiety
Your Stone Age Brain (CYP)
Your Stone Age Brain (CYP)
Understanding Generalized Anxiety And Worry
Understanding Generalized Anxiety And Worry
Understanding Social Anxiety
Understanding Social Anxiety
Therapy Blueprint For Social Anxiety
Therapy Blueprint For Social Anxiety
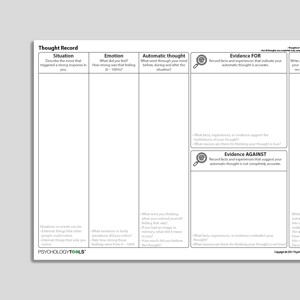
Thought Record (Evidence For And Against)
Thought Record (Evidence For And Against)
Cognitive Behavioral Model of Perfectionism (Shafran, Egan, Wade, 2010)
Cognitive Behavioral Model of Perfectionism (Shafran, Egan, Wade, 2010)
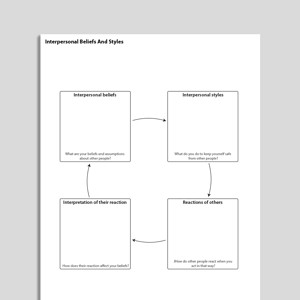
Interpersonal Beliefs And Styles
Interpersonal Beliefs And Styles
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Intolerance Of Uncertainty And Generalized Anxiety Disorder Symptoms (Hebert, Dugas, 2019)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Intolerance Of Uncertainty And Generalized Anxiety Disorder Symptoms (Hebert, Dugas, 2019)
[Free Guide] Living With Worry And Anxiety Amidst Global Uncertainty
[Free Guide] Living With Worry And Anxiety Amidst Global Uncertainty
Intolerance Of Uncertainty
Intolerance Of Uncertainty
What Does Exercise Do For the Mind And Body?
What Does Exercise Do For the Mind And Body?
Exercise For Mental Health
Exercise For Mental Health
Mindfulness In Everyday Life (Audio)
Mindfulness In Everyday Life (Audio)
Mindfulness Of Breath (Long Version) (Audio)
Mindfulness Of Breath (Long Version) (Audio)
Mindfulness Of Sounds And Thoughts (Audio)
Mindfulness Of Sounds And Thoughts (Audio)
Mindfulness Of Breath (Short Version) (Audio)
Mindfulness Of Breath (Short Version) (Audio)
Trauma, Dissociation, And Grounding (Archived)
Trauma, Dissociation, And Grounding (Archived)
Transdiagnostic Processes
Transdiagnostic Processes
Testing Anxious And Panicky Predictions (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
Testing Anxious And Panicky Predictions (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
Approach Instead Of Avoiding (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
Approach Instead Of Avoiding (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
Coping With Body Sensations (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
Coping With Body Sensations (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
Working With Anxious Thoughts And Predictions (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
Working With Anxious Thoughts And Predictions (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
Breathing To Calm The Body Sensations Of Panic (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
Breathing To Calm The Body Sensations Of Panic (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
Making Sense Of Your Panic (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
Making Sense Of Your Panic (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
The Parts Of Your Panic (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
The Parts Of Your Panic (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
Monitoring Your Panic (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
Monitoring Your Panic (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
How Much Do You Know About Panic? (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
How Much Do You Know About Panic? (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
Why Do I Keep Getting Panic Attacks? (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
Why Do I Keep Getting Panic Attacks? (Psychology Tools For Overcoming Panic)
Links to external resources
Psychology Tools makes every effort to check external links and review their content. However, we are not responsible for the quality or content of external links and cannot guarantee that these links will work all of the time.
Assessment
-
Oxford - Agoraphobic Avoidance Scale (O-AS)
| Lambe, S., Bird, J. C., Loe, B. S., Rosebrock, L., Kabir, T., Petit, A., ... & Freeman, D. | 2023
- Scale
- Reference Lambe, S., Bird, J. C., Loe, B. S., Rosebrock, L., Kabir, T., Petit, A., ... & Freeman, D. (2023). The Oxford agoraphobic avoidance scale. Psychological Medicine, 53(4), 1233-1243.
-
Brief Fear of Negative Evaluation Scale
| Leary | 1983
- Scale
-
Severity Measure For Agoraphobia
| Craske, Wittchen, Bogels, Stein, Andrews, Lebu | 2013
- Scale – Adult
-
Social Phobia Scale
| Mattick, Clarke | 1995
- Scale
-
Social Phobia Inventory (SPIN)
| Connor, Davidson, Churchill, Sherwood, Weisler, Foa | 2000
- Scale
-
Severity Measure For Specific Phobia
| Craske, Wittchen, Bogels, Stein, Andrews, Lebeu | 2013
- Scale – Adult
- Scale – Child Age 11-17
-
Severity Measure For Social Anxiety Disorder
| Craske, Wittchen, Bogels, Stein, Andrews, Lebeu | 2013
- Scale – Adult
- Scale – Child Age 11-17
-
Severity Measure For Panic Disorder
| Craske, Wittchen, Bogels, Stein, Andrews, Lebeu | 2013
- Scale – Adult
-
Severity Measure For Generalized Anxiety Disorder
| Craske, Wittchen, Bogels, Stein, Andrews, Lebeu | 2013
- Scale – Adult
- Scale – Child Age 11-17
-
Spence Children’s Anxiety Scale
| Spence | 1998
- Spence, S. H. (1998). A measure of anxiety symptoms among children. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 36 (5), 545-566.
- Scale
- Scale website link
-
Penn State Worry Questionnaire
| Meyer, Miller, Metzger, Borkovec | 1990
- Meyer, T. J., Miller, M. L., Metzger, R. L., & Borkovec, T. D. (1990). Development and validation of the penn state worry questionnaire. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 28(6), 487-495.
- Scale archive.org
-
Panic Disorder Severity Scale (PDSS)
| Shear, Brown, Barlow, Money, Sholomskas, Woods, Gorman, Papp | 1997
- Shear, M. K., Brown, T. A., Barlow, D. H., Money, R., Sholomskas, D. E., Woods, S. W., … & Papp, L. A. (1997). Multicenter collaborative panic disorder severity scale. American Journal of Psychiatry, 154(11), 1571-1575.
- Scale
-
Mobility Inventory For Agoraphobia(MIA)
| Chambless, Caputo, Jasin, Gracely, Williams | 1985
- Chambless, D. L., Caputo, G. C., Jasin, S. E., Gracely, E. J., & Williams, C. (1985). The mobility inventory for agoraphobia. Behaviour research and therapy, 23(1), 35-44.
- Scale
-
Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale (LSAS-SR)
| Liebowitz | 1987
- Scale
-
Health Anxiety Inventory (HAI-18)
| Salkovskis, Rimes, Warwick, Clark | 2002
- Scale
- Reference Salkovskis, P. M., Rimes, K. A., Warwick, H. M. C., & Clark, D. M. (2002). The Health Anxiety Inventory: development and validation of scales for the measurement of health anxiety and hypochondriasis. Psychological Medicine, 32(05), 843-853.
-
Hamilton Rating Scale For Anxiety (HAM-A)
| Hamilton | 1959
- Hamilton, M. (1959).The assessment of anxiety states by rating. British Journal of Medical Psychology 32, 50-55.
- Scale
-
Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item (GAD-7)
| Spitzer, Kroenke, Williams, Lowe | 2006
- Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JBW, Lowe B. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder. Arch Inern Med. 2006;166:1092-1097.
- Scale
-
Fear Questionnaire (FQ) (Phobia)
| Marks, Matthews | 1979
- Marks, I. M., & Mathews, A. M. (1979). Brief standard self-rating for phobic patients. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 17(3), 263-267.
- Scale
- Brief Fear Of Negative Evaluation Scale | Leary | 1983
Guides and workbooks
- Anxiety And Substance Use | NDARC: Mills, Marel, Baker, Teesson, Dore, Kay-Lambkin, Manns, Triningham | 2011
- Specific phobia: patient treatment manual | Clinical Research Unit for Anxiety and Depression (CRUfAD)
- Working To Overcome Anxiety (Workbook) | Lucock, Noble, Pallister, Horsefield, Padgett, Westley, Atha, Khan | 2015
- Social Anxiety (An NHS Self-Help Guide) | Lesley Maunder, Lorna Cameron | 2020
- Phobia Self-Help Booklet | Anne Joice, Jim White | 2006
- Panic attacks: what they are and how to stop the next one | Glasgow STEPS
- Coping with panic | Charles Young, Alison Hunte, Jessica Newell, Pat Valian | 2011
- Health Anxiety – A Self-Help Guide | Maunder, Cameron, Young, Leyland | 2015
Information Handouts
-
Panic (Information Handouts)
| Centre For Clinical Interventions
- What Is Panic?
- Biology and Psychology of Panic
- The Vicious Cycle of Anxiety
- Breathing Retraining
- Behavioural Experiments (Negative Predictions)
- Situational Exposure
- Physical Sensations and Panic
- What Are Safety Behaviours?
-
Health Anxiety (Information Handouts)
| Centre For Clinical Interventions
- What is health anxiety?
- What are safety behaviors?
- Dealing with health information
-
Social Anxiety (Information Handouts)
| Centre For Clinical Interventions
- What is social anxiety?
- What can be done about social anxiety?
- Breathing retraining
- Progressive muscle relaxation
- Improving how you feel
- Thinking and feeling
- Analysing your thinking
- Changing your thinking
- Unhelpful thinking styles
- What are core beliefs?
- Situational exposure
- What are safety behaviors?
- Staying healthy
-
Anxiety (Information Handouts)
| Centre For Clinical Interventions
- What is anxiety?
- The vicious cycle of anxiety
- Analysing your thinking
- Unhelpful thinking styles
- Behavioral experiments
- Situational exposure
- What are safety behaviours?
- Breathing retraining
- Progressive muscle relaxation
- Stress and anxiety
- Coping with stress
- Anxiety and exercise
- What is needle phobia?
- Overcoming needle phobia
- CBT for anxiety
Information (Professional)
- Task Concentration Training Definition | Bögels
- Interoceptive Exposure Definition | White, Basden, Barlow
- Assertive defense of the self (A more effective treatment focus for social phobia?) | Padesky | 1985
Presentations
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapies for Social Anxiety Disorder: Integrating the 3 Waves of Evidence-Based Therapy | Larry Cohen | 2022
- Why worry? Key cognitive processes that maintain worry and Generalised Anxiety Disorder | Colette Hirsch
- New developments in exposure therapy for anxiety and related disorders: the inhibitory learning approach | Blakey, Abramowitz | 2018
- Bringing Specificity to Generalized Anxiety Disorder: Conceptualization and Treatment of GAD using Intolerance of Uncertainty as the Theme of Threat | Robichaud | 2013
- GAD – a cognitive model and treatment
- Desirable difficulties: optimizing exposure therapy for anxiety through inhibitory learning | Abramowitz, Jacoby, Blakey | 2018
Self-Help Programmes
-
What? Me Worry? (Workbook)
| Centre For Clinical Interventions | 2015
- Module 1: Overview Of Generalized Anxiety
- Module 2: Overview Of Worrying
- Module 3: Challenging Uncontrollability Beliefs
- Module 4: Attention Training
- Module 5: Challenging Danger Beliefs
- Module 6: Challenging Positive Beliefs
- Module 7: Problem-Solving
- Module 8: Helpful Thinking
- Module 9: Accepting Uncertainty
- Module 10: Self Management Plan
-
Stepping Out Of Social Anxiety (Workbook)
| Centre For Clinical Interventions | 2020
- Module 1: Understanding Social Anxiety
- Module 2: Overcoming Negative Thinking
- Module 3: Overcoming Avoidance
- Module 4: Behavioral Experiment Stepladders
- Module 5: Safety Behaviors
- Module 6: The Role Of Attention
- Module 7: How I Think I Appear To Others
- Module 8: Challenging Core Beliefs
- Module 9: Strengthening New Core Beliefs
- Module 10: Maintaining Your Gains And Dealing With Setbacks
-
When Panic Attacks (Workbook)
| Centre For Clinical Interventions | 2023
- Module 1: Overview Of Panic
- Module 2: What Keeps Panic Disorder Going
- Module 3: Overcoming Thoughts About Panic
- Module 4: Coping With Physical Alarms
- Module 5: Facing Feared Situations
- Module 6: Dropping Safety Behaviors
- Module 7: Maintaining Your Gains
Treatment Guide
- Comprehensive cognitive behavior therapy for social phobia: a treatment manual | Deborah Roth Ledley, Edna B. Foa, Jonathan D. Huppert (in consultation with David M. Clark) | 2005
- Cognitive behavioral therapy for anxiety: an application of the F.E.A.R. model for adults | Stephen Lenz
- The CARS cognitive behavioral treatment for anxiety manual | Center for Adolescent Research in Schools | 2014
- Canadian clinical practice guidelines for the management of anxiety, posttraumatic stress and obsessive-compulsive disorders (2014) | Katzman et al | 2014
- Panic disorder: Manual for Improving Access to Psychological Therapy (IAPT) High intensity CBT therapists. | David Clark, Paul Salkovskis | 2009
- Comprehensive cognitive behavior therapy for social phobia: a treatment manual | Ledley, Foa, Huppert, Clark | 2006
- NICE Guidelines For Social Anxiety Disorder | NICE | 2013
- NICE Guidelines For GAD And Panic | NICE | 2011
- A brief cognitive-behavioural treatment for social anxiety disorder | Eric P. Morris, David Mensink, and Sherry H. Stewart
Worksheets
-
Panic (Worksheets)
| Centre For Clinical Interventions
- Breathing Rate Record
- Anxiety Symptoms
- Monitoring Relaxation
- Situational Exposure Diary
- Internal Exposure Record
-
Social Anxiety (Worksheets)
| Centre For Clinical Interventions
- Anxiety symptoms record
- Breathing rate record
- Monitoring your relaxation level
- Weekly activity schedule
- Weekly goals record
- Making the connection
- Thought diary 1
- Thought diary 2
- Thought diary 3
- Thought diary (tri-fold)
- Core beliefs worksheet
- Situational exposure: building steps
- Behavioral experiments
- Healthy me
- Goal setting: end of therapy
-
Anxiety (Worksheets)
| Centre For Clinical Interventions
- Anxiety Symptoms Record
- Breathing Rate Record
- Monitoring Relaxation
- Situational Exposure Diary
- Making The Connection
- Thought Diary 1
- Thought Diary 2
- Thought Diary 3
- Thought Diary (Tri-Fold)
- Behavioral Experiment Worksheet
Recommended Reading
Health anxiety
- Walker, J. R., Furer, P. (2008). Interoceptive exposure in the treatment of health anxiety and hypochondirasis. Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy, 22(4), 366-378
Social Anxiety Disorder
- Warnock-Parkes, E., Wild, J., Thew, G., Kerr, A., Grey, N., & Clark, D. (2022). ‘I’m unlikeable, boring, weird, foolish, inferior, inadequate’: How to address the persistent negative self-evaluations that are central to social anxiety disorder with cognitive therapy. The Cognitive Behaviour Therapist, 15, E56. doi:10.1017/S1754470X22000496 view
- Warnock-Parkes, E., Wild, J., Stott, R., Grey, N., Ehlers, A., & Clark, D. M. (2017). Seeing is believing: Using video feedback in cognitive therapy for social anxiety disorder. Cognitive and behavioral practice, 24(2), 245-255. view
- Veale, D. (2003). Treatment of social phobia. Advances in Psychiatric Treatment, 9, 258-264
- Wild, Hackmann, Clark (2008). Rescripting early memories linked to negative images in social phobia: a pilot study. Behaviour Therapy, 39(1), 47-56.
- Moscovitch, D. A. (2009). What is the core fear in social phobia? A new model to facilitate individualized case conceptualization and treatment. Cognitive and Behavioural Practice, 16. 123-134
- Clark, D. M. (2001). A cognitive perspective on social phobia
Panic disorder
- Wells, A. (1997). Cognitive Therapy of Anxiety Disorders. Chichester: Wiley.
- Schmidt, N. B., Woolaway-Bickel, K., Trakowski, J. et al. (2000). Dismantling cognitive-behavioural treatment for panic disorder: Questioning the utility of breathing retraining. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 68(3), 417-424
- Huppert, J. D., & Baker-Morissette, S. L. (2003). Beyond the manual: The insider’s guide to panic control treatment.Cognitive and Behavioral Practice,10(1), 2-13.
- Clark, D. A. (1999). Anxiety disorders: Why they persist and how to treat them. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 37, S5-S27
Health anxiety
- Salkovskis, P. M., Warwick, H. M. C., Deale, A. C. (2003). Cognitive-Behavioral Treatment for Severe and Persistent Health Anxiety (Hypochondriasis). Brief Treatment and Crisis Intervention, 3, 353-367 btci.edina.clockss.org
- Furer, P., Walker, J. R. (2008). Death anxiety: A cognitive behavioural approach. Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy, 22(2), 167-182
- Asmundson, G. J. G., Abramowitz, J. S., Richter, A. A., Whedon, M. (2010). Health anxiety: current perspectives and future directions. Current Psychiatry Reports, 12, 306-312
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
- Roemer, L., Salters, K., Raffa, S. D., & Orsillo, S. M. (2005). Fear and avoidance of internal experiences in GAD: Preliminary tests of a conceptual model.Cognitive Therapy and Research,29(1), 71-88.
- Roemer, L., & Orsillo, S. M. (2002). Expanding our conceptualization of and treatment for generalized anxiety disorder: Integrating mindfulness/acceptance‐based approaches with existing cognitive‐behavioral models.Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice,9(1), 54-68
- Mennin, D. S., Heimberg, R. G., Turk, C. L., & Fresco, D. M. (2002). Applying an emotion regulation framework to integrative approaches to generalized anxiety disorder.Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice,9(1), 85-90
- Fresco, D. M., Mennin, D. S., Heimberg, R. G., & Ritter, M. (2013). Emotion regulation therapy for generalized anxiety disorder.Cognitive and Behavioral Practice,20(3), 282-300 nih.gov
- Wells, A. (1995). Meta-cognition and worry: A cognitive model of generalized anxiety disorder.Behavioural and cognitive psychotherapy,23(3), 301-320
- Hjemdal, O., Hagen, R., Nordahl, H. M., & Wells, A. (2013). Metacognitive therapy for generalized anxiety disorder: Nature, evidence and an individual case illustration.Cognitive and Behavioral Practice,20(3), 301-313.
- Hjemdal, O., Hagen, R., Nordahl, H. M., & Wells, A. (2013). Metacognitive therapy for generalized anxiety disorder: Nature, evidence and an individual case illustration.Cognitive and Behavioral Practice,20(3), 301-313
- Borkovec, T. D., Alcaine, O., & Behar, E. (2004). Avoidance theory of worry and generalized anxiety disorder.Generalized anxiety disorder: Advances in research and practice,2004.
- Dugas, M. J., Gagnon, F., Ladouceur, R., & Freeston, M. H. (1998). Generalized anxiety disorder: A preliminary test of a conceptual model.Behaviour research and therapy,36(2), 215-226.
- Milne, S., Lomax, C., & Freeston, M. H. (2019). A review of the relationship between intolerance of uncertainty and threat appraisal in anxiety. the Cognitive Behaviour Therapist, 12.
- Hirsch, C. R., Beale, S., Grey, N., & Liness, S. (2019). Approaching cognitive behavior therapy for generalized anxiety disorder from a cognitive process perspective. Frontiers in psychiatry, 10, 796.
- Bottesi, G., Ghisi, M., Carraro, E., Barclay, N., Payne, R., & Freeston, M. H. (2016). Revising the Intolerance of Uncertainty Model of Generalized Anxiety Disorder: Evidence from UK and Italian Undergraduate Samples.Frontiers in psychology,7, 1723
- Behar, E., DiMarco, I. D., Hekler, E. B., Mohlman, J., Staples, A. M. (2009). Current theoretical models of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD): Conceptual review and treatment implications. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 23, 1011-1023
General
- Clark, D. M. (1999). Anxiety disorders: why they persist and how to treat them. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 37, S5-S27
- Task concentration training and fear of blushing | Bögels, Mulkens, De Jong | 1997
What Is Anxiety?
Signs and Symptoms of Anxiety Disorders
Different anxiety disorders are characterized by various foci of concern.Health anxiety is characterized by concern about one’s health or illness.
Panic attacks are characterized by an abrupt surge or intense fear.
palpitations or accelerated heart rate
sweating
trembling or shaking
dry mouth
difficulty breathing
a feeling of choking
nausea or abdominal discomfort
dizziness
derealization or depersonalization
fear of losing control or passing out
fear of dying
hot flushes or cold chills
numbness or tingling
blushing
fear of vomiting
urgency or fear of urination or defecation
Psychological Models and Theories of Anxiety
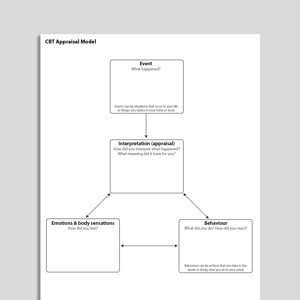
One broad conceptualization of anxiety can be summarized by an ‘anxiety equation’ (Beck, Emery, & Greenberg, 1985; Salkovskis, Forrester, & Richards, 1998):Anxiety = (perceived probability of therapy × perceived cost or awfulness of danger)÷ (perceived ability to cope + perceived ‘rescue factors’)Disorder-specific ‘CBT for anxiety’ cognitive models have been developed for all of the anxiety disorders. These are helpful in that they direct the therapist’s attention toward key interpretations and behaviors that act to perpetuate the anxiety disorders. For example, the critical mechanism that Clark identified in the cognitive model of panic (1986) is that body sensations are misinterpreted catastrophically as signs of danger, with concomitant effects upon emotions, behavior, and secondary cognitions.
Evidence-Based Psychological Approaches for Working with Anxiety
Cognitive behavior therapy has a strong evidence base for treating all of the anxiety disorders. Key components of CBT for anxiety interventions include exposure to the feared situations or stimulus, and an experimental approach to test the accuracy of beliefs.Resources for Working with Anxiety
Psychology Tools resources available for working therapeutically with anxiety may include:psychological models of anxiety
exercises for anxiety
CBT worksheets for anxiety
self-help programs for anxiety including a guide to overcoming panic attacks and panic disorder
References
Beck, A. T., Emery, G., & Greenberg, R. L. (1985). Anxiety disorders and phobias: A cognitive perspective. New York: Basic Books.
Clark, D. M. (1986). A cognitive approach to panic. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 24(4), 461–470.
Salkovskis, P. M., Forrester, E., & Richards, C. (1998). Cognitive–behavioral approach to understanding obsessional thinking. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 173(S35), 53–63.
















![[Free Guide] Living With Worry And Anxiety Amidst Global Uncertainty](https://media-engine-production-public.s3.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com/28433/conversions/%2A-guide_to_living_with_worry_and_anxiety_amidst_global_uncertainty_en-gb_Guides_Cover-preview.jpg)