Addictions Worksheets, Dual Diagnosis, And Relapse Prevention
Misuse of alcohol and other drugs frequently co-occurs with other mental health conditions. For example, rates of PTSD among some groups misusing substances have been reported to be as high as 50% (Reynolds et al., 2005). Mental health professionals working with substance misuse use a variety of psychological approaches. These include cognitive behavioral techniques, relapse prevention, motivational interviewing, and solution-focused brief therapy.
Showing 1 to 50 of 64 results
Manage Your Mind: The Mental Fitness Guide (Third Edition)
Manage Your Mind: The Mental Fitness Guide (Third Edition)
Transdiagnostic LGBTQ-Affirmative Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy: Client Workbook
Transdiagnostic LGBTQ-Affirmative Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy: Client Workbook
Transdiagnostic LGBTQ-Affirmative Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy: Therapist Guide
Transdiagnostic LGBTQ-Affirmative Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy: Therapist Guide
Insufficient Self-Control
Insufficient Self-Control
Dependence / Incompetence
Dependence / Incompetence
Approval-/Admiration-Seeking
Approval-/Admiration-Seeking
Urges – Self-Monitoring Record
Urges – Self-Monitoring Record
Magnification And Minimization
Magnification And Minimization
Permissive Thinking – Self-Monitoring Record
Permissive Thinking – Self-Monitoring Record
Audio Collection: Psychology Tools For Mindfulness
Audio Collection: Psychology Tools For Mindfulness
Managing Your Substance Use Disorder (Third Edition): Workbook
Managing Your Substance Use Disorder (Third Edition): Workbook
Managing Substance Use Disorder (Third Edition): Practitioner Guide
Managing Substance Use Disorder (Third Edition): Practitioner Guide
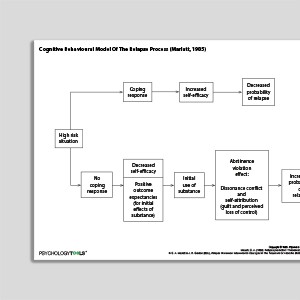
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of The Relapse Process (Marlatt & Gordon, 1985)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of The Relapse Process (Marlatt & Gordon, 1985)
Boundaries - Self-Monitoring Record
Boundaries - Self-Monitoring Record
Grounding Techniques Menu
Grounding Techniques Menu
Mindfulness In Everyday Life (Audio)
Mindfulness In Everyday Life (Audio)
Mindfulness Of Sounds And Thoughts (Audio)
Mindfulness Of Sounds And Thoughts (Audio)
Mindfulness Of Breath (Long Version) (Audio)
Mindfulness Of Breath (Long Version) (Audio)
Mindfulness Of Breath (Short Version) (Audio)
Mindfulness Of Breath (Short Version) (Audio)
A Guide To Emotions (Psychology Tools For Living Well)
A Guide To Emotions (Psychology Tools For Living Well)
Sensory Grounding Using Your Five Senses (Audio)
Sensory Grounding Using Your Five Senses (Audio)
Sensory Grounding Using Smells (Audio)
Sensory Grounding Using Smells (Audio)
Relaxed Breathing Exercise 4 (Audio)
Relaxed Breathing Exercise 4 (Audio)
Relaxed Breathing Exercise 3 (Audio)
Relaxed Breathing Exercise 3 (Audio)
Links to external resources
Psychology Tools makes every effort to check external links and review their content. However, we are not responsible for the quality or content of external links and cannot guarantee that these links will work all of the time.
Assessment
-
Drinking motives questionnaire – adolescent
| Cooper | 1994
- Cooper, M.L. (1994). Motivations for alcohol use among adolescents: Development and validation of a four-factor model. Psychological Assessment, 6,117-128.
- Scale
-
Leeds Dependence Questionnaire
| Raistrick, Bradshaw, Tober, Weiner, Allison, Healey | 1994
- Raistrick, D.S., Bradshaw, J., Tober, G., Weiner, J., Allison, J. & Healey, C. (1994) Development of the Leeds Dependence Questionnaire, Addiction, 89, pp 563-572.
- Scale
-
Maudsley Addiction Profile (MAP)
| Marsden, Gossop, Stewart, Best, Farrell, Lehmann, Edwards, Strang | 1998
- Marsden, J. Gossop, M. Stewart, D. Best, D. Farrell, M. Lehmann, P. Edwards, C. & Strang, J. (1998) The Maudsley Addiction Profile (MAP): A brief instrument for assessing treatment outcome, Addiction 93(12): 1857-1867.
- Scale
-
Readiness to Change Questionnaire (RTQ)
| Heather, Rollnick | 1993
- Rollnick, Heather, Gold, Hall (1992)
- User’s manual
-
Severity of Dependence Scale
| Gossop, Darke, Griffiths, Hando, Powis, Hall, Strang | 1995
- Scale
- Gossop, M., Darke, S., Griffiths, P., Hando, J., Powis, B., Hall, W., Strang, J. (1995). The Severity of Dependence Scale (SDS): psychometric properties of the SDS in English and Australian samples of heroin, cocaine and amphetamine users. Addiction 90(5): 607-614.
-
Stages of Change Readiness and Treatment Eagerness Scale (SOCRATES)
| Miller, Tonigan | 1996
- Scale
- Reference Miller, W. R., & Tonigan, J. S. (1996). Assessing drinkers’ motivation for change: the Stages of Change Readiness and Treatment Eagerness Scale (SOCRATES). Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 10(2), 81.
-
Drinking motives questionnaire
| Cooper, Russell, Skinner, Windle | 1992
- Cooper, M. L., Russell, M., Skinner, J. B., & Windle, M. (1992). Development and validation of a three-dimensional measure of drinking motives. Psychological Assessment,4,123-132.
- Scale
Guides and workbooks
- Psychosis And Substance Use | NDARC: Mills, Marel, Baker, Teesson, Dore, Kay-Lambkin, Manns, Trimingham | 2011
- Trauma And Substance Use | NDARC: Mills, Ewer, Marel, Baker, Teesson, Dore, Kay-Lambkin, Manns, Trimmingham | 2011
- Changing Addictive Thought Patterns | Mayo Clinic
- Personality And Substance Use | NDARC: Mills, Marel, Baker, Teesson, Dore, Kay-Lambkin, Manns, Trimingham | 2011
- Alcohol And You (An NHS Self-Help Guide) | Holdsworth, Anslow, Crawford, Hall, Jcques, McNally, Reynolds, Widdas, Maunder, Cameron | 2020
- Anxiety And Substance Use | NDARC: Mills, Marel, Baker, Teesson, Dore, Kay-Lambkin, Manns, Triningham | 2011
- Mood And Substance Use | NDARC: Mills, Marel, Baker, Teesson, Dore, Kay-Lambkin, Manns, Trimingham | 2011
Information Handouts
- What Is Alcoholism? | NACOA
- Introduction To Codependency | NACOA
Presentations
- What to do if CBT isn’t working | Bruce Liese | 2020
- Cognitive behavioral & relapse prevention strategies | UNODC | 2007
- The great porn experiment – TED lecture | Gary Wilson
Treatment Guide
- Counselor’s Manual For Relapse Prevention With Chemically Dependent Criminal Offenders | USDHHS | 1996
- Enhancing motivation to change in substance use disorder treatment | SAMHSA | 2019
- Individualized treatment for problem gamblers: patient workbook | Timothy W. Fong, Richard J. Rosenthal | 2009
- Integrated cognitive behavior therapy: clinician's manual | Mark McGovern, Kim Mueser, Jessica Hamblen, Mary Jankowski
- Cognitive Behavioural Coping Skills Treatment Manual: A clinical research guide for therapists treating individuals with alcohol abuse and dependence | Kadden, Carroll, Donovan, Cooney, Monti, Abrams, Litt, Hester | 2003
- Enhancing Motivation for Change in Substance Use Disorder Treatment | SAMHSA | 2019
- Motivational Enhancement Therapy Manual | Miller, Zweben, DiClemente, Rychtarik | 1995
- Clinical guidelines for implementing relapse prevention therapy | Marlatt, Parks, Witkiewitz | 2002
- A Cognitive-Behavioral Approach: Treating Cocaine Addiction (National Institute On Drug Abuse: Therapy Manuals For Drug Addiction) | Kathleen Carroll | 1998
- Patient’s workbook for cognitive behavioral therapy sessions – Intensive Treatment and rehabilitation program for residential treatment and rehabilitation centers for drug dependents (INTREPRET) | Phillipines Department of Health | 2020
- Substance use / brain injury bridging project – Client workbook | Community Head Injury Resource Services of Toronto (CHIRS) and the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH)
- Substance Use / Brain Injury Workbook | Community Head Injury Resource Services of Toronto (CHIRS), Centre For Addiction And Mental Health (CAMH)
Recommended Reading
- Brownell, K. D., Marlatt, G. A., Lichtenstein, E., & Wilson, G. T. (1986). Understanding and preventing relapse.American Psychologist,41(7), 765.
- Hendershot, C. S., Witkiewitz, K., George, W. H., & Marlatt, G. A. (2011). Relapse prevention for addictive behaviors.Substance abuse treatment, prevention, and policy,6(1), 17.
- Larimer, M. E., Palmer, R. S., Marlatt, G. A. (1999). An overview of Marlatt’s Cognitive-Behavioural Model. Alcohol Research and Health, 23(2), 151-160
- Volkow, N. D., Koob, G. F., & McLellan, A. T. (2016). Neurobiologic advances from the brain disease model of addiction. New England Journal of Medicine, 374(4), 363-371
- Addictions And Trauma Recovery (Paper Presented At The International Society For The Study Of Dissociation) | Janina Fischer | 2000
What Is Addiction?
Signs and Symptoms of Addictions and Relapse
Behavioral and Social Signs of Addictions Include:
Continuing to use a substance (or engage in certain behaviors) despite the negative consequences that they cause
Trying but failing to reduce or stop misusing a substance
Secretive, furtive, or dishonest behavior
Psychological Symptoms of Addictions Include:
Mood swings
Anger or irritability
Paranoia
Defensiveness
Poor judgment
Psychological Models of Addictions and Relapse
There is considerable psychological theory which clinicians working in the field of addiction can draw upon.
Prochaska and DiClemente’s Transtheoretical Model (Stages of Change Model)
The transtheoretical model (Prochaska & DiClemente, 1982; Prochaska, DiClemente, Norcross, 1992) is used to conceptualize the process of intentional behavior change. It identifies important stages in the process of changing a behavior: precontemplation, contemplation, preparation, action, and maintenance. The transtheoretical model also identifies processes which need to be implemented to attain behavior change: consciousness raising (awareness of the facts), dramatic relief (paying attention to feelings), environmental re-evaluation (noticing our effects upon others), self–re-evaluation (creating a new self-image), social liberation (noticing support around us), self-liberation (making a commitment), counterconditioning (using substitutes), helping relationships (getting support), reinforcement management (using rewards), stimulus control (managing your environment).
Marlatt and Gordon’s Cognitive Behavioral Model of Relapse
Marlatt and Gordon published a cognitive behavioral model of relapse in 1985. They conceptualize relapse as a “transitional process, a series of events that unfold over time” (Marlatt & Gordon, 1985). The model identifies factors that can contribute toward episodes of relapse. These include intrapersonal factors such as self-efficacy (the degree to which an individual feels confident and capable of performing a certain behavior in a specific situational context), outcome expectancies (an individual’s anticipation of the effects of a future experience), craving, motivation, and social support.
The Cognitive Behavioral Model of Substance Abuse
The cognitive behavioral model of substance abuse (Beck, Wright, Newman, & Liese, 1993) describes psychological areas of vulnerability that predispose an individual to misusing substances including: dysfunctional beliefs about drugs, oneself, or one’s relationship with drugs; ‘permission-giving beliefs’ with which an individual may justify their drug use; and reactions to a lapse or relapse that lead to a vicious cycle of maintenance.
Evidence-Based Psychological Approaches for Working with Addictions and Relapse
Cognitive approaches to working with addictions may include:
identifying patterns of dysfunctional thinking such as ‘permission-giving beliefs’;
learning how to delay and distract in response to cravings and urges;
making positive lifestyle changes;
treating underlying mental health conditions which predispose an individual toward substance misuse.
Resources for Working with Addictions and Relapse
Psychology Tools resources available for working therapeutically with addictions may include:
psychological models of addiction and relapse
information handouts for addiction and relapse
exercises for addiction and relapse
CBT worksheets for addiction and relapse
self-help programs for addiction and relapse
References
Beck, A. T., Wright, F., Newman, C., & Liese, B. (1993). Cognitive therapy of substance abuse: a treatment manual. New York Guilford.
Larimer, M. E., & Palmer, R. S. (1999). Relapse prevention: An overview of Marlatt’s cognitive-behavioral model. Alcohol Research and Health, 23(2), 151–160.
Marlatt, G. A. (1985). Relapse prevention: Theoretical rationale and overview of the model. In G. A. Marlatt & J. R. Gordon (Eds.), Relapse prevention. New York: Guilford Press.
Prochaska, J. O., & DiClemente, C. C. (1982). Transtheoretical therapy: Toward a more integrative model of change. Psychotherapy: Theory, Research & Practice,19(3), 276–288.
Prochaska, J. O., DiClemente, C. C., & Norcross, J. C. (1992). In search of how people change: Applications to the addictive behaviors. American Psychologist, 47(9), 1102–1114.
Reynolds, M., Mezey, G., Chapman, M., Wheeler, M., Drummond, C., & Baldacchino, A. (2005). Co-morbid post-traumatic stress disorder in a substance misusing clinical population. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 77(3), 251–258.