Avoidance and Escape
- avoidance and escape behaviors remove the opportunity to disconfirm negative beliefs (Salkovskis, 1991);
- they reduce an individual’s opportunities to obtain positive reinforcement and thus contribute to the maintenance of low mood (Ferster, 1973; Lewinsohn, 1975);
- they reduce the number of external stimuli present in an individual’s environment (‘shrinks their world’) which may exacerbate self-focused attention and repetitive thinking (Harvey, Watkins, Mansell, & Shafran, 2004);
- according to a habituation model of anxiety the relatively brief exposure periods occasioned by escape and avoidance may server to ‘sensitize’ patients to their feared stimuli (Wilson & O’Leary, 1980).

Choosing Your Values
Fight Or Flight Response
Assertive Communication
Window Of Tolerance
Embracing Uncertainty
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) Formulation
Intolerance Of Uncertainty
Values: Connecting To What Matters
Activity Menu
Social Anxiety Formulation
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Formulation
Behavioral Activation Activity Diary
Unified Protocol for Transdiagnostic Treatment of Emotional Disorders (Second Edition): Client Workbook
Behavioral Experiment (Portrait Format)
Behavioral Experiment
Health Anxiety Formulation
Fear Ladder
Panic Formulation
Changing Avoidance (Behavioral Activation)
Treating Your OCD With Exposure And Response (Ritual) Prevention (Second Edition): Workbook
What Is Worry?
Exposure And Response Prevention
Mastery Of Your Anxiety And Worry (Second Edition): Workbook
What Keeps Depression Going?
Unified Protocol for Transdiagnostic Treatment of Emotional Disorders (Second Edition): Therapist Guide
Habituation
Understanding Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Exposure Session Record
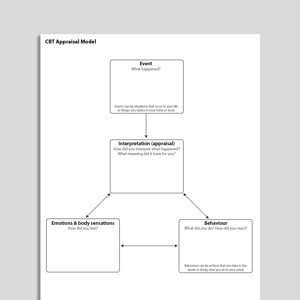
CBT Appraisal Model
Behavioral Activation Activity Planning Diary
Understanding Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Audio Collection: Psychology Tools For Overcoming PTSD
Mastery Of Your Anxiety And Panic (Fifth Edition): Workbook
Understanding Health Anxiety
OCD Hierarchy
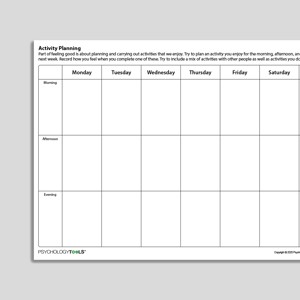
Activity Planning
Understanding Social Anxiety
Understanding Depression
What Keeps Social Anxiety Going?
Interoceptive Exposure
Problem Solving
Exposure And Response (Ritual) Prevention For Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (Second Edition): Therapist Guide
Mastery Of Your Anxiety And Worry (Second Edition): Therapist Guide
Activity Diary (Hourly Time Intervals)
Overcoming Your Eating Disorder: Workbook
Exposure Practice Form
Managing Social Anxiety (Third Edition): Workbook
Thought Suppression And Intrusive Thoughts
Uncertainty Beliefs – Experiment Record
Reclaiming Your Life From A Traumatic Experience (Second Edition): Workbook
Autonomic Nervous System
Pacing For Pain And Fatigue
Self-Monitoring Record (Universal)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD: Ehlers & Clark, 2000)
Your Stone Age Brain
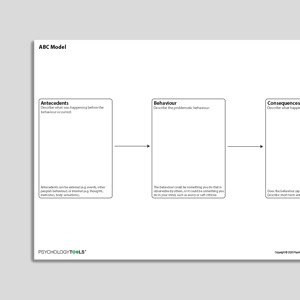
ABC Model
Safety Behaviors
What Keeps Death Anxiety Going?
Stages Of Social Anxiety
Fight or Flight (CYP)
Cognitive Behavioral Treatment of Childhood OCD: It's Only a False Alarm: Workbook
Mastery Of Your Anxiety And Panic (Fifth Edition): Therapist Guide
What Keeps Panic Going?
Overcoming Eating Disorders (Second Edition): Therapist Guide
Maximizing The Effectiveness Of Exposure Therapy
Facing Your Fears And Phobias
Understanding Death Anxiety
Managing Social Anxiety (Third Edition): Therapist Guide
Understanding Panic
Prolonged Exposure Therapy For PTSD (Second Edition): Therapist Guide
Avoidance Hierarchy (Archived)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Health Anxiety (Salkovskis, Warwick, Deale, 2003)
What Keeps Fears And Phobias Going?
A Guide To Emotions (Psychology Tools For Living Well)
Your Stone Age Brain (CYP)
Panic Attack Record
Cognitive Behavioral Treatment Of Childhood OCD: It's Only A False Alarm: Therapist Guide
Problem Solving (CYP)
Facing Your Fears (CYP)
Critical Care And PTSD
Understanding Fears And Phobias
Panic - Self-Monitoring Record
What Are Safety Behaviors?
Process Focused Case Formulation
Activity Diary (No Time Intervals)
Am I Experiencing Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)?
Mastery And Pleasure Activity Diary
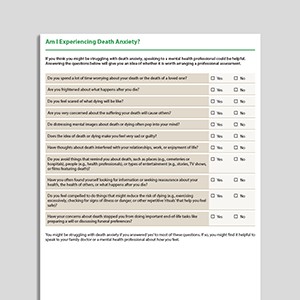
Am I Experiencing Death Anxiety?
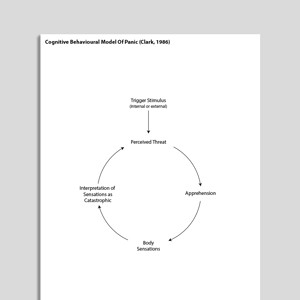
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Panic (Clark, 1986)
Being With Difficulty (Audio)
Critical Illness Intensive Care And Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
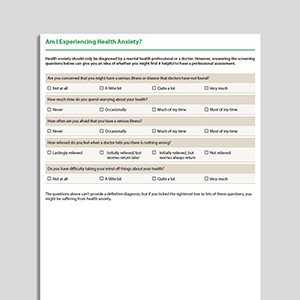
Am I Experiencing Health Anxiety?
Transdiagnostic Processes
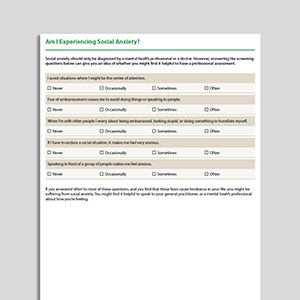
Am I Experiencing Social Anxiety?
Activity Selection
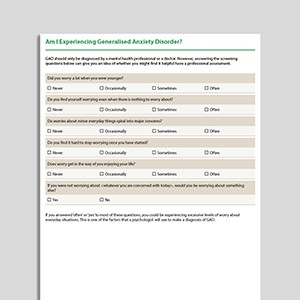
Am I Experiencing Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)?
Starvation Syndrome – The Effects of Semi-Starvation
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Social Phobia (Clark, Wells, 1995)
Am I Experiencing Depression?
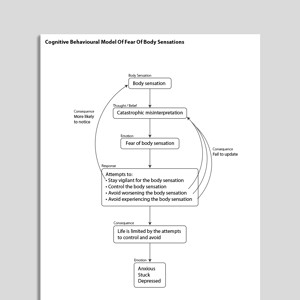
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Fear Of Body Sensations
Links to external resources
Psychology Tools makes every effort to check external links and review their content. However, we are not responsible for the quality or content of external links and cannot guarantee that these links will work all of the time.
Assessment
-
Oxford - Agoraphobic Avoidance Scale (O-AS)
| Lambe, S., Bird, J. C., Loe, B. S., Rosebrock, L., Kabir, T., Petit, A., ... & Freeman, D. | 2023
- Scale
- Reference Lambe, S., Bird, J. C., Loe, B. S., Rosebrock, L., Kabir, T., Petit, A., ... & Freeman, D. (2023). The Oxford agoraphobic avoidance scale. Psychological Medicine, 53(4), 1233-1243.
Exercises
- Facing your fears: Exposure | Anxiety Canada
What Are Avoidance And Escape?
Disorders That May Be Maintained by Avoidance and Escape
Avoidance and escape are often maintenance factors in:
- panic disorder with or without agoraphobia
- specific phobia
- social phobia
- obsessive compulsive disorder
- post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and acute stress disorder
- generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
- pain disorder
- health anxiety
- body dysmorphic disorder
- eating disorders
- depression
- psychotic disorders
- substance abuse disorders
Helpful Questions for Assessing Avoidance and Escape
Some helpful questions for assessing avoidance and escape include:
- How do you respond when you feel threatened?
- What activities/people/places/situations/objects do you avoid?
- What does the avoidance get in the way of you doing?
- What would happen if you stopped avoiding?
Treatment Approaches That Target Avoidance and Escape
Exposure is often considered the method of choice to reduce avoidance across the anxiety disorders. Varieties of exposure techniques include in-vivo exposure, graded exposure, and interoceptive exposure. Mowrer’s two-stage model of fear and avoidance is cited as the origin of the behavioral practice of reducing avoidance (Mowrer, 1939, 1960). According to this theory, avoidance behavior is reinforced when it is followed by a reduction in anxiety.
Cognitive techniques have also been found to be highly effective treatments for anxiety, with successful treatment leading to reductions in avoidance (Kaczkurkin & Foa, 2015).
References
- Ferster, C. B. (1973). A functional analysis of depression. American Psychologist, 28(10), 857–870.
- Harvey, A. G., Watkins, E., Mansell, W., & Shafran, R. (2004). Cognitive behaviouralprocesses across psychological disorders: A transdiagnostic approach to research and treatment. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Kaczkurkin, A. N., & Foa, E. B. (2015). Cognitive-behavioral therapy for anxiety disorders: an update on the empirical evidence. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 17(3), 337–346.
- Lewisohn, P. M. (1975). Engagement in pleasant activities and depression level. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 84(6), 729–731.
- Mowrer, O. H. (1939). Anxiety and learning. Psychological Bulletin, 36, 517–518.
- Mowrer, O. H. (1960). Learning theory and behavior. New York: Wiley.
- Salkovskis, P. M. (1991). The importance of behaviourin the maintenance of anxiety and panic: A cognitive account. Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy, 19(1), 6–19.
- Wilson, G. T. and O’Leary, D. (1980). Principles of behavior therapy. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.