Cognitive Distortion / Cognitive Bias
Human beings are processing information all of the time: in both a fast and automatic fashion, and as slow and effortful process (e.g., Kahneman, 2011). In the context of psychological therapy the term cognitive bias refers to the ability that people have to selectively attend to and recall information, or to distort information. Clinically, the most widely known aspect of cognitive bias are the cognitive distortions (unhelpful thinking styles) identified by Beck, examples of which include arbitrary inference, over-generalization, and dichotomous thinking (Beck, 1963). Harvey, Watkins, Mansell, and Shafran (2004) define reasoning as “thinking that is concerned with deducing conclusions, generating judgements, and testing hypotheses in a logical and coherent way.” They go on to describe a number of ways in which reasoning processes can become biased with the frequent “result that the conclusion drawn differs from objective reality”. Biases in reasoning or information processing are not necessarily dysfunctional but they often play important roles in maintaining clinical problems, including anxiety and mood disorders. Some forms of cognitive bias which are important in CBT include:
Read more

99 of 99 resources
"Should" Statements
“Should” statements (sometimes referred to as ‘musturbation’, ‘necessitous thinking’, ‘self-commands’, and ‘injunctions’) are char ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/should-statements
All-Or-Nothing Thinking
All-or-nothing thinking (often also referred to as ‘black and white thinking’, ‘dichotomous thinking’, ‘absolutist thinking’, or ‘binary ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/all-or-nothing-thinking
Am I Experiencing Burnout?
‘Burnout’ is characterized by feeling emotionally drained, unmotivated, and ineffective as a result of prolonged stress during work. This can impa ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/am-i-experiencing-burnout
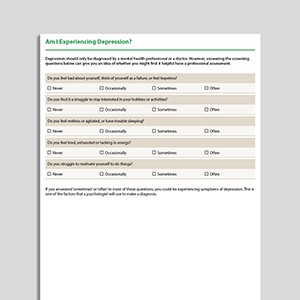
Am I Experiencing Depression?
Depression is a condition characterized by an extended period of low mood, anhedonia, and reduction in activity. Am I Experiencing Depression? is an i ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/am-i-experiencing-depression
Anger Thought Challenging Record
Evaluating and disputing thoughts is a fundamental skill taught by cognitive therapists to their clients. The Anger Thought Challenging Record can hel ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/anger-thought-challenging-record
Anxiety - Self-Monitoring Record
Developing self-monitoring skills teaches clients to systematically observe and record specific targets such as their own thoughts, body feelings, emo ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/anxiety-self-monitoring-record
Arbitrary Inference
Arbitrary inference is one of the earliest and broadest cognitive disotortions described in CBT. Beck defines it as "the process of forming an interpr ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/arbitrary-inference
Before I Blame Myself And Feel Guilty
Guilt is a common post-traumatic reaction and is often the result of cognitive bias. This CBT worksheet explores common cognitive biases that have bee ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/before-i-blame-myself-and-feel-guilty
Behavioral Experiment
Behavioral experiments are planned experiential activities to test the validity of a belief. They are one of the most powerful techniques available to ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/behavioral-experiment
Behavioral Experiment (Portrait Format)
Behavioral experiments allow individuals to test the validity of their beliefs and assumptions. They are a core experiential technique for therapeutic ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/behavioral-experiment-portrait-format
Belief Driven Formulation
Cognitive behavioral theory proposes that our thoughts, feelings, and behavior in the here-and-now are influenced by our schemas / core beliefs / assu ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/belief-driven-formulation
Belief-O-Meter (CYP)
The Belief-O-Meter is an engaging way of helping children and adolescents to relate to their thoughts differently. It is a form of cognitive restructu ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/belief-o-meter-cyp
Catastrophizing
The Catastrophizing information handout forms part of the cognitive distortions series. It is designed to help clients and therapists to work more eff ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/catastrophizing
Catching Your Thoughts (CYP)
Before thoughts can be examined or challenged they must be ‘caught’ – they must be noticed and distinguished from events and feelings. The Catch ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/catching-your-thoughts-cyp
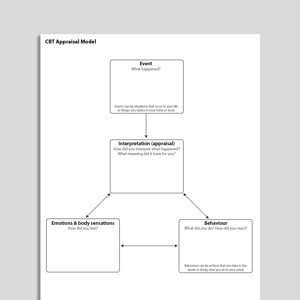
CBT Appraisal Model
The CBT Appraisal Model worksheet is a transdiagnostic formulation tool. The centrality of appraisals underpins all of the disorder-specific cognitive ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/cbt-appraisal-model
CBT Thought Record Portrait
The CBT Thought Record is an essential tool in cognitive behavioral therapy. Thought challenging records help people to evaluate their negative automa ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/cbt-thought-record-portrait
Challenging Your Negative Thinking (Archived)
NOTE: An improved version of this resource is available here: Evaluating Unhelpful Automatic Thoughts. Older versions of a resource may be archived in ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/challenging-your-negative-thinking
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Anorexia Nervosa (Fairburn, Cooper, Shafran, 2003)
Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by restriction of energy intake and intense fear of gaining weight. For women, the lifetime preva ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/cognitive-behavioral-model-of-anorexia-nervosa-fairburn-cooper-shafran-2003
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD: Veale, 2004)
Individuals with body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) experience distress associated with their body image. The Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Body Dysmorphi ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/cognitive-behavioral-model-of-body-dysmorphic-disorder-bdd-veale-2004
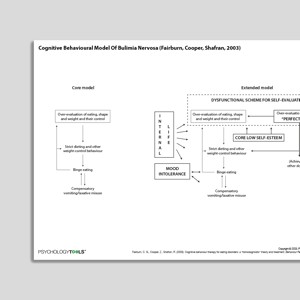
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Bulimia Nervosa (Fairburn, Cooper, Shafran, 2003)
Bulimia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating followed by purging. Among young women, the point prevalence of bulimia is about 1 ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/cognitive-behavioral-model-of-bulimia-nervosa-fairburn-cooper-shafran-2003
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Health Anxiety (Salkovskis, Warwick, Deale, 2003)
Health anxiety is characterized by a preoccupation with having or acquiring a serious illness, and a high level of anxiety about health. People with h ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/cognitive-behavioral-model-of-health-anxiety-salkovskis-warwick-deale-2003
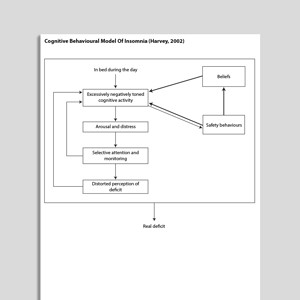
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Insomnia (Harvey, 2002)
Insomnia is a highly prevalent sleep disorder characterized by difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, or having non-restorative sleep for at leas ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/cognitive-behavioral-model-of-insomnia-harvey-2002
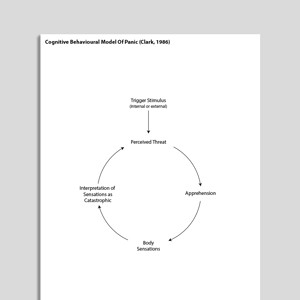
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Panic (Clark, 1986)
The Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Panic identifies catastrophic misinterpretation of body sensations as a criticial maintenance factor which serves to ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/cognitive-behavioral-model-of-panic-clark-1986
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD: Ehlers & Clark, 2000)
Anke Ehlers' & David Clark's Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is an influential account of the condition. The ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/cognitive-behavioral-model-of-post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd-ehlers-clark-2000
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Social Phobia (Clark, Wells, 1995)
People suffering from social anxiety disorder (previously known as social phobia) experience persistent fear or anxiety concerning social or performan ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/cognitive-behavioral-model-of-social-phobia-clark-wells-1995
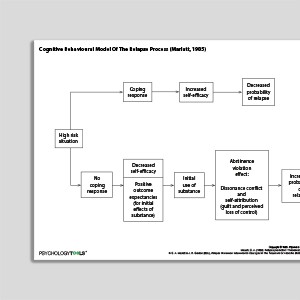
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of The Relapse Process (Marlatt & Gordon, 1985)
Marlatt & Gordon’s cognitive behavioral model of relapse (1985) conceptualizes relapse as a “transitional process, a series of events that unf ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/cognitive-behavioural-model-of-the-relapse-process-marlatt-gordon-1985
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Tinnitus (McKenna, Handscombe, Hoare, Hall, 2014)
The Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Tinnitus identifies cognitive, behavioral, and perceptual changes which operate to maintain tinnitus perception and ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/cognitive-behavioral-model-of-tinnitus-mckenna-handscombe-hoare-hall-2014
Cognitive Distortions – Unhelpful Thinking Styles (Common)
Cognitive distortions (or ‘unhelpful thinking styles’) are ways that our thoughts become biased. Different cognitive biases are associated with di ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/cognitive-distortions-unhelpful-thinking-styles-common
Cognitive Distortions – Unhelpful Thinking Styles (Extended)
Cognitive distortions (or ‘unhelpful thinking styles’) are ways that our thoughts become biased. Different cognitive biases are associated with di ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/cognitive-distortions-unhelpful-thinking-styles-extended
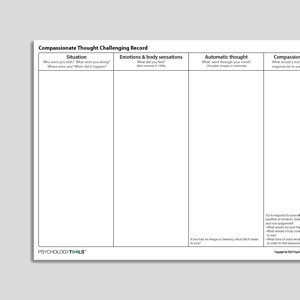
Compassionate Thought Challenging Record
Thought challenging records are commonly used in CBT to help people to evaluate their negative automatic thoughts for accuracy and bias. This Compassi ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/compassionate-thought-challenging-record
Core Belief Magnet Metaphor
Core beliefs (schemas) are self-sustaining. They act to 'attract' confirmatory evidence and 'repel' (or distort) disconfirmatory evidence. This inform ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/core-belief-magnet-metaphor
Court Trial Thought Challenging Record (Archived)
NOTE: An improved version of this resource is available here: Thought Record - Courtroom Trial. Older versions of a resource may be archived in the ev ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/court-trial-thought-challenging-record
Decatastrophizing
Catastrophic thinking (magnification) is characteristic of many anxiety problems. This CBT worksheet for decatastrophizing is a tool for cognitive res ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/decatastrophizing
Depression - Self-Monitoring Record
Developing self-monitoring skills teaches clients to systematically observe and record specific targets such as their own thoughts, body feelings, emo ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/depression-self-monitoring-record
Disqualifying Others
This Disqualifying Others information handout forms part of the cognitive distortions series, designed to help clients and therapists to work more eff ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/disqualifying-others
Disqualifying The Positive
This Disqualifying the Positive information handout forms part of the cognitive distortions series, designed to help clients and therapists work more ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/disqualifying-the-positive
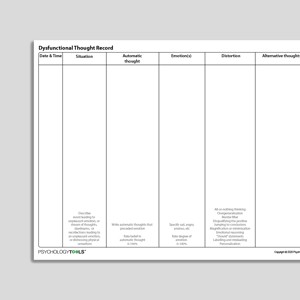
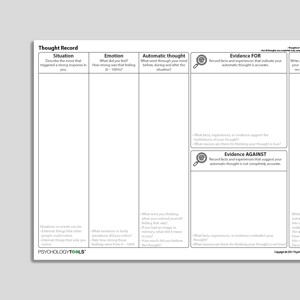
Dysfunctional Thought Record
The Dysfunctional Thought Record is a worksheet to record and challenge dysfunctional thoughts. It encourages clients to identify the involvement of a ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/dysfunctional-thought-record
Emotional Reasoning
The Emotional Reasoning information handout forms part of the cognitive distortions series, designed to help clients and therapists to work more effec ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/emotional-reasoning
Evaluating Unhelpful Automatic Thoughts
The Evaluating Unhelpful Automatic Thoughts guide is written for clients who struggle with negative automatic thoughts. It provides a comprehensive in ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/evaluating-unhelpful-automatic-thoughts
Examining Your Negative Thoughts
Cognitive restructuring is an evidence-based intervention that involves identifying, evaluating, and modifying maladaptive cognitions, including negat ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/examining-your-negative-thoughts
Externalizing
The Externalizing information handout forms part of the cognitive distortions series, designed to help clients and therapists to work more effectively ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/externalizing
Fact Or Opinion
One cognitive error which commonly results in distress is to act on our opinions as though they were facts. This CBT exercise helps clients to practic ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/fact-or-opinion
Fortune Telling
The Fortune Telling information handout forms part of the cognitive distortions series, designed to help clients and therapists to work more effective ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/fortune-telling
Health Anxiety Thought Record
Individuals with health anxiety experience clinically significant distress associated with health concerns. This thought-challenging record enables cl ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/health-anxiety-thought-record
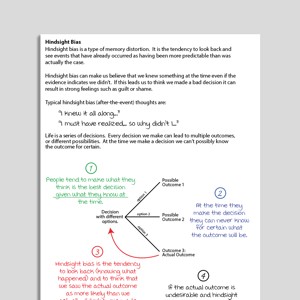
Hindsight Bias
Hindsight bias describes the tendency that people have – once an outcome is known – to believe that they predicted (or could have predicted) an ou ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/hindsight-bias
Hindsight Bias (Archived)
Survivors of loss or trauma often think "If only …". Hindsight Bias is a cognitive bias / cognitive illusion which makes events seem more predictabl ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/hindsight-bias-archived
How Trauma Can Affect You (CYP)
Trauma can result in a wide variety of symptoms, experiences, and behaviors. As well as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), prevalence rates of oth ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/how-trauma-can-affect-you-cyp
Identifying The Meaning Of Body Sensations
Some anxiety disorders (including panic and health anxiety), are concerned with body sensations and symptoms. The Identifying The Meaning Of Body Sens ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/identifying-the-meaning-of-body-sensations
Jumping To Conclusions
The Jumping to Conclusions information handout forms part of the cognitive distortions series, designed to help clients and therapists to work more ef ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/jumping-to-conclusions
Labeling
Identifying negative automatic thoughts and reappraising unhelpful thinking is a core element of cognitive therapy. Teaching clients to recognize the ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/labeling
Low Self-Esteem Formulation
Fennell’s cognitive behavioral model of low self-esteem proposes that negative beliefs about the self are maintained by biased information processin ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/low-self-esteem-formulation
Magnification And Minimization
The Magnification And Minimization information handout forms part of the cognitive distortions series, designed to help clients and therapists to work ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/magnification-and-minimization
Managing Social Anxiety (Third Edition): Therapist Guide
Managing Social Anxiety – A Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy Approach comes in two volumes. This page is for the Therapist Guide. Click on the following ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/managing-social-anxiety-therapist-guide
Mastery Of Your Anxiety And Panic (Fifth Edition): Therapist Guide
Mastery Of Your Anxiety And Panic comes in two volumes. This page is for the Therapist Guide. Click on the following link to access the accompanying C ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/mastery-of-your-anxiety-and-panic-therapist-guide
Mastery Of Your Anxiety And Panic (Fifth Edition): Workbook
Mastery Of Your Anxiety And Panic comes in two volumes. This page is for the Workbook. Click on the following link to access the accompanying Therapis ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/mastery-of-your-anxiety-and-panic-workbook
Meaning In Tinnitus
The psychological approach to tinnitus proposes that it is the meaning attached to perceptions which gives rise to distress - this is similar to the a ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/meaning-in-tinnitus
Mental Filter
The Mental Filter information handout forms part of the cognitive distortions series, designed to help clients and therapists to work more effectively ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/mental-filter
Mind Reading
The Mind Reading information handout forms part of the cognitive distortions series, designed to help clients and therapists to work more effectively ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/mind-reading
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) Formulation
An important treatment implication of the cognitive behavioral model of OCD is that clinicians can work at the level of the meaning of the intrusion. ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/obsessive-compulsive-disorder-ocd-formulation
Overcoming Depression (Second Edition): Therapist Guide
Overcoming Depression – A Cognitive Therapy Approach comes in two volumes. This page is for the Therapist Guide. Click on the following link to acce ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/overcoming-depression-therapist-guide
Overcoming Depression (Second Edition): Workbook
Overcoming Depression – A Cognitive Therapy Approach comes in two volumes. This page is for the Client Workbook. Click on the following link to acce ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/overcoming-depression-workbook
Overcoming Eating Disorders (Second Edition): Therapist Guide
Overcoming Eating Disorders comes in two volumes. This page is for the Therapist Guide. Click on the following link to access the Client Workbook.&nbs ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/overcoming-eating-disorders-therapist-guide
Overcoming Insomnia (Second Edition): Therapist Guide
Overcoming Insomnia comes in two volumes. This page is for the Therapist Guide. Click on the following link to access the Client Workbook. It is ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/overcoming-insomnia-therapist-guide
Overcoming Insomnia (Second Edition): Workbook
Overcoming Insomnia comes in two volumes. This page is for the Client Workbook. Click on the following link to access the accompanying Therapist Guide ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/overcoming-insomnia-workbook
Overcoming Your Eating Disorder: Workbook
Overcoming Eating Disorders comes in two volumes. This page is for the Client Workbook. Click on the following link to access the accompanying Therapi ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/overcoming-your-eating-disorder-workbook
Overgeneralization
The Overgeneralization information handout forms part of the cognitive distortions series, designed to help clients and therapists to work more effect ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/overgeneralization
Panic - Self-Monitoring Record
Developing self-monitoring skills teaches clients to systematically observe and record specific targets such as their own thoughts, body feelings, emo ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/panic-self-monitoring-record
Panic Attack Record
Self-monitoring of thoughts, feelings, and symptoms is an essential skill for clients engaged in cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). The Panic Attack ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/panic-attack-record
Permissive Thinking
The Permissive Thinking information handout forms part of the cognitive distortions series, designed to help clients and therapists to work more effec ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/permissive-thinking
Permissive Thinking – Self-Monitoring Record
Developing self-monitoring skills teaches clients to systematically observe and record specific targets such as their own thoughts, body feelings, emo ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/permissive-thinking-self-monitoring-record
Personalizing
The Personalizing information handout forms part of the cognitive distortions series, designed to help clients and therapists to work more effectively ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/personalizing
Positive Belief Record
Some cognitive change can happen quickly - for example challenging negative automatic thoughts. Other cognitive structures such as schemas are more de ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/positive-belief-record
Process Focused Case Formulation
The Process-Focused Case Formulation encourages clinicians to make hypotheses regarding mechanisms or processes which they believe may be maintainin ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/process-focused-case-formulation
Prolonged Exposure Therapy For PTSD (Second Edition): Therapist Guide
Prolonged Exposure Therapy For PTSD comes in two volumes. This page is for the Therapist Guide. Click on the following link to access the accompanying ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/prolonged-exposure-therapy-for-ptsd-therapist-guide
Prompts For Challenging Negative Thinking (Archived)
NOTE: An improved version of this resource is available here: Prompts For Challenging Negative Thinking. Older versions of a resource may be arch ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/prompts-for-challenging-negative-thinking-archived
Prompts For Challenging Your Negative Thinking
Cognitive restructuring is an evidence-based intervention that involves identifying, evaluating, and modifying maladaptive cognitions, including negat ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/prompts-for-challenging-your-negative-thinking
PTSD Formulation
This PTSD Formulation is designed for use in trauma-focused cognitive therapy for PTSD (CT-PTSD): an empirically supported treatment for post-traumati ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/ptsd-formulation
Schema Formulation
Beck's cognitive model proposes that cognition and perception in the here-and-now are influenced by our 'schemas', which shape our perception and info ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/schema-formulation
Schema Metaphors
Core beliefs (schemas) are self-sustaining. They act to 'attract' confirmatory evidence and 'repel' or 'distort' disconfirmatory evidence. This inform ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/schema-metaphors
Self-Blame
The Self-Blame information handout forms part of the cognitive distortions series, designed to help clients and therapists to work more effectively wi ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/self-blame
Self-Monitoring Record (Universal)
Developing self-monitoring skills teaches clients to systematically observe and record specific targets such as their own thoughts, body feelings, emo ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/self-monitoring-record-universal
Simple Thought Challenging Record
Disputing thoughts is a critical skill in cognitive therapy. The Simple Thought Challenging Record encourages clients to identify alternative perspect ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/simple-thought-challenging-record
Simple Thought Record
Self-monitoring of thoughts, feelings, and symptoms is an essential skill in cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). This Simple Thought Record is an exce ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/simple-thought-record
Social Anxiety Formulation
People suffering from social anxiety disorder (previously known as social phobia) experience persistent fear or anxiety concerning social or performan ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/social-anxiety-formulation
Social Comparison
The Social Comparison information handout forms part of the cognitive distortions series, designed to help clients and therapists to work more effecti ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/social-comparison
Thought Distortion Monitoring Record
Thinking is often biased in particular ways and individuals often have their own characteristic patterns of bias. The Thought Distortion Monitoring Re ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/thought-distortion-monitoring-record
Thought Record (Considered Response)
Thought records exist in multiple variants, depending on the needs and abilities of the client. This Thought Record (Considered Response) is a cogniti ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/thought-record-considered-response
Thought Record (Evidence For And Against)
CBT Thought Records exist in multiple variants, depending on the needs and abilities of the client. This Thought Record (Evidence For And Against) is ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/thought-record-evidence-for-and-against
Thought-Action Fusion
The Thought-Action Fusion information handout forms part of the cognitive distortions series, designed to help clients and therapists to work more eff ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/thought-action-fusion
Thoughts And Depression
Depression is associated with cognitive biases, one of which is a failure to notice positive information. This information handout presents this conce ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/thoughts-and-depression
Thoughts In CBT (Psychology Tools For Living Well)
Cognitive behavioral therapy can help your clients to live happier and more fulfilling lives. Psychology Tools for Living Well is a self-help course ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/thoughts-in-cbt-psychology-tools-for-living-well
Understanding Depression
Our ‘Understanding…’ series is a collection of psychoeducation guides for common mental health conditions. Friendly and explanatory, they are co ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/understanding-depression
Understanding Panic
Our ‘Understanding…’ series is a collection of psychoeducation guides for common mental health conditions. Friendly and explanatory, they are co ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/understanding-panic
Unhelpful Thinking Styles (Archived)
NOTE: Two improved versions of this resource are available here: Cognitive Distortions – Unhelpful Thinking Styles (Common) and Cognitive Disto ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/unhelpful-thinking-styles-archived
Unified Protocol for Transdiagnostic Treatment of Emotional Disorders (Second Edition): Client Workbook
The Unified Protocol for Transdiagnostic Treatment of Emotional Disorders (Second Edition) comes in two volumes. This page is for the Client Workbook. ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/unified-protocol-for-transdiagnostic-treatment-of-emotional-disorders-second-edition-client-workbook
Unified Protocol for Transdiagnostic Treatment of Emotional Disorders (Second Edition): Therapist Guide
The Unified Protocol for Transdiagnostic Treatment of Emotional Disorders (Second Edition) comes in two volumes. This page is for the Therapist Guide. ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/unified-protocol-for-transdiagnostic-treatment-of-emotional-disorders-second-edition-therapist-guide
What Is Memory?
Like other aspects of cognition, transient difficulties with memory can be caused by stress or fatigue and there is a documented decline in memory fun ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/what-is-memory
What Keeps Depression Going?
The “What Keeps It Going?” series is a set of one-page diagrams explaining how common mental health conditions are maintained. Friendly and concis ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/what-keeps-depression-going
What Keeps Low Self-Esteem Going?
The “What Keeps It Going?” series is a set of one-page diagrams explaining how common mental health conditions are maintained. Friendly and concis ...
https://www.psychologytools.com/resource/what-keeps-low-self-esteem-going
Links to external resources
Psychology Tools makes every effort to check external links and review their content. However, we are not responsible for the quality or content of external links and cannot guarantee that these links will work all of the time.
Information Handouts
-
Unhelpful Thinking Styles (Information Handouts)
| Centre For Clinical Interventions
- Mental Filter
- Jumping To Conclusions
- Personalisation
- Catastrophizing
- Black And White Thinking
- Shoulding And Musting
- Overgeneralization
- Labelling
- Emotional Reasoning
- Magnification And Minimisation
- Challenging Unhelpful Thinking Styles
Recommended Reading
- Beck, A. T., Rush, A. J., Shaw, B. F., Emery, G. (1979). Cognitive therapy of depression. New York: Guilford
- Burns, D. D. (1980. Feeling good. New York: Avon Books
What Is Cognitive Bias?
Disorders That May Be Maintained by Cognitive Bias
Cognitive biases, including biased interpretations, attributions, expectancies, or heuristics, are thought to contribute to the maintenance of:
- panic disorder (interpretation bias, attribution bias, expectancy bias, emotional reasoning);
- specific phobia (expectancy bias, emotional reasoning);
- social phobia (interpretation bias, attribution bias, expectancy bias);
- obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) (attribution bias, expectancy bias, emotional reasoning);
- post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) (interpretation bias, attribution bias, expectancy bias, emotional reasoning);
- generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) (interpretation bias, attribution bias, expectancy bias, emotional reasoning);
- pain disorder (interpretation bias, expectancy bias);
- health anxiety (interpretation bias, attribution bias, expectancy bias);
- eating disorders (interpretation bias, attribution bias, expectancy bias);
- depression (interpretation bias, attribution bias, expectancy bias);
- bipolar disorder (attribution bias);
- psychosis (interpretation bias, attribution bias, expectancy bias);
- substance misuse (interpretation bias, attribution bias, expectancy bias).
Helpful Questions for Assessing Cognitive Bias
Some helpful questions for assessing cognitive bias:
- What do you think will happen if you do X or Y?
- What predictions are you making in this situation?
- What sort of evidence are you using to make this judgment or prediction?
- What do you expect will happen here?
- How do you know what will happen?
Treatment Approaches That Target Cognitive Bias
A wide range of treatment interventions are designed to target cognitive bias. These can include:
- data gathering exercises that aim to overcome attentional biases;
- thought-challenging exercises that aim to identify and then overcome cognitive distortions;
- exposure and behavioral experiments that target expectancy biases.
References
- Beck, A. T. (1963). Thinking and depression: I. Idiosyncratic content and cognitive distortions. Archives of General Psychiatry, 9(4), 324–333.
- Harvey, A. G., Watkins, E., Mansell, W., & Shafran, R. (2004). Cognitive behaviouralprocesses across psychological disorders: A transdiagnostic approach to research and treatment. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Kahneman, D. (2011). Thinking, fast and slow. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux.